Content
- Overview
- Models
- UML
- Static (Structure)
- Dynamic (Behavior)
- UML Sequence Diagram
- System Sequence Diagram (SSD)
- The Domain Model
- Steps
Overview
Analysis is a modelling activity. From use case model & SRS, break down the problem and produce new models of it.
- Better understand the problem
- Reveal remaining defects || omissions in the spec
- Good foundation for design
Models
- Structured (function-oriented) analysis
- Data flow diagram
- State-transition diagram
- Entity-relationship diagram
- Object-oriented analysis
- Unified modelling language (UML)
- Produces domain model (static)
UML

Static (Structure)
- Class diagram
- Types of objects
- Attributes
- Operations of classes
Dynamic (Behavior)
- Sequence diagram
- How objects collaborate via messages to produce behavior
- May add state machine diagram to model object lifecycles
UML Sequence Diagram
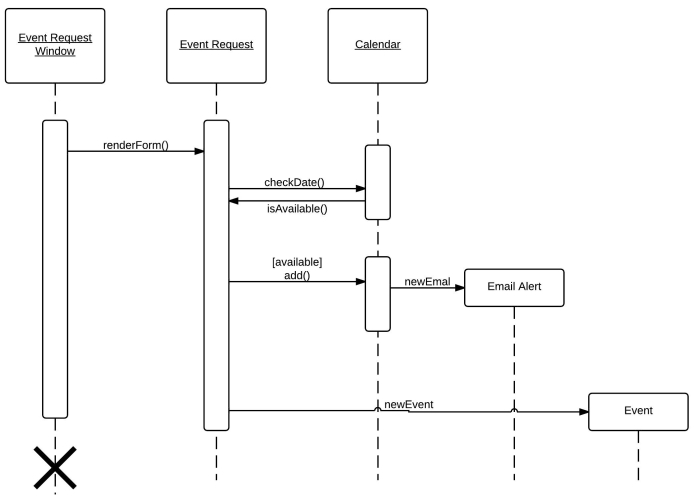
- Notations
Class:Instancei:NamedInstanceReturn = message_name (parameter : parameterType, ...) : returnType|| dashed-arrow back- Full arrow: synchronous; open arrow: asynchronous
- Arrow back to denote
this - Dashed full arrow to denote
<<create>> <<destroy>>
System Sequence Diagram (SSD)
We use the UML sequence diagram to show a time-ordering of events and responses.
- System treated as black-box
- Only constructed for main success scenarios of non-trivial use cases || frequent and complex alternate scenarios
- Easy to generate from use case descriptions
The Domain Model
- Conceptual Classes (domain objects)
- Physical
- Conceptual
- Associations between conceptual classes
- Attributes of conceptual classes
Only focus on problem space during analysis. No software domain included.
Steps
- Identify conceptual classes
- Use class category list
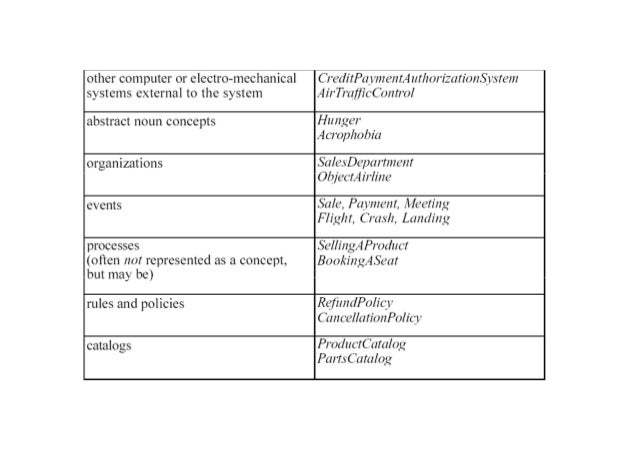
- Identify nouns or noun phrases in scenario descriptions
- Eliminate candidates:
- Redundant
- Instances of class
- Vague
- An event or operation
- Outside of scope
- An attribute
- Eliminate candidates:
- Use class category list
- Add attributes
- What we need to satisfy the information requirements
- Should be simple (UML data types) & lack identity
- Some non-meaningful yet not good attributes:
- Composed of separate sections (Address)
- Associated with operations such as validation (HKID)
- Quantity with a unit (Money)
- Has attributes of its own
- Add associations & constraints

- Multiplicity (cardinality)
- Number of instances that can validly be associated with another at a particular moment, NOT over a span of time
- Naming association || end names (label)
- Usefulness
- Multiplicity (cardinality)