Content
- Overview
- Risk Exposure
- Risk Mitigation
- Types of Risk
- Technical/Product Risk
- Non-Technical Risk
- Risk Profile
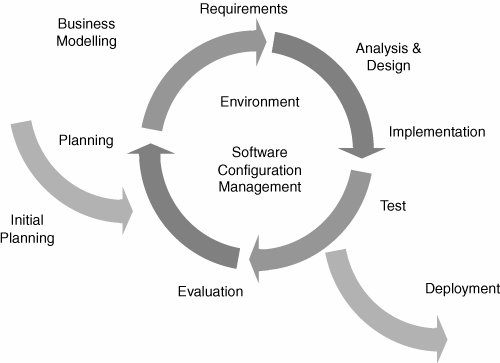
- Iterative & Incremental Process
- Risk Driven
- Iterative Cycle
- Benefits
Overview
- Potential problem -> loss & threat to success of project
- Adverse impact on cost, schedule, technical success, quality
Risk Exposure
- Uncertainty
- No 100% risks; they would be constraints
- Impact
- Risk exposure = uncertainty * impact
Risk Mitigation
- Risk avoidance
- Risk limitation/reduction
- Reduce probability or impact
- Rick transfer
- Not a full transfer
- Make it someone else's problem who can better manage it
- Risk acceptance
- Monitor & rely on contingency action if risk materializes
Types of Risk
Technical/Product Risk
- New Technology adopted or needed
- Architecture supporting required functionality, suitability of framework, ability to meet quality requirements
- Building the right system, identify true functional & non-functional requirements
Risk-driven & client-driven:
maintain requirements in a separate list other than the risk list, prioritized by importance to client.
Non-Technical Risk
- Project risk
- Schedule, resources
- Business risk
Real risks but not useful for driving actual development.
Identified, tracked, and handled by managers.
Usually out-of-scope when planning development work.
Risk Profile

Iterative & Incremental Process
- Develop in a sequence of iterations (small, self-contained mini-projects)
- Setting goals for each iteration at the start of iteration -> deal with change
- Deliverable of each iteration is a working release: stable, integrated, tested, partially complete
- An iteration builds on top of the previous iteration
- Additional advantage: users cannot wait for fully functional system to be developed
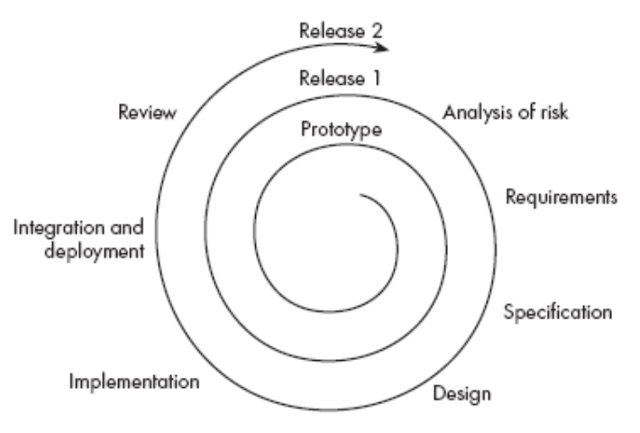
Risk Driven
Do the most critical & uncertain stuff first.
-> Identify & ------> Select next incremental step ------> develop executable
prioritize risks to deal with the next highest risk that eliminates the risk
↑__________________________________________________________|
Iterative Cycle
Benefits
- Early mitigation of big risks
- Early visible progress
- Early feedback, user engagement, adaptation
- Complexity managed (no attempt to do all analysis up-front)
- Experience during an iteration helps improve later iterations