Monochrome Image
Intensity
I(x, y)
Intensity (grey level) of the image at point (x, y).
- Amount of source light incident on the scene
- Amount of light reflected by the objects in the scene
Digitizing an Image
When x, y, and I(x, y) are finite & discrete quantities, the image is a digital image.
- Digitizing coordinates: sampling
- Digitizing intensity values: quantization
Representation
$$ I(i, j) = \begin{bmatrix}
I{0,0} & \dots & I{0, M-1} \ \vdots & \ddots & \vdots \ I{N-1,0} & \dots & I{n-1, M-1} \
\end{bmatrix}
$$
Quality
- Spatial resolution
- $$N \times M$$
- Problem
- Sampling checkerboards
- Gray-level resolution
- 256: 8-bit image
- Problem
- False contouring
Pixel
Neighbor
Pixel p at (x, y).
- 4-neighbors $$N_4(p)$$
- Diagonal neighbors $$N_D(p)$$
- 8-neighbors $$N_8(p)$$
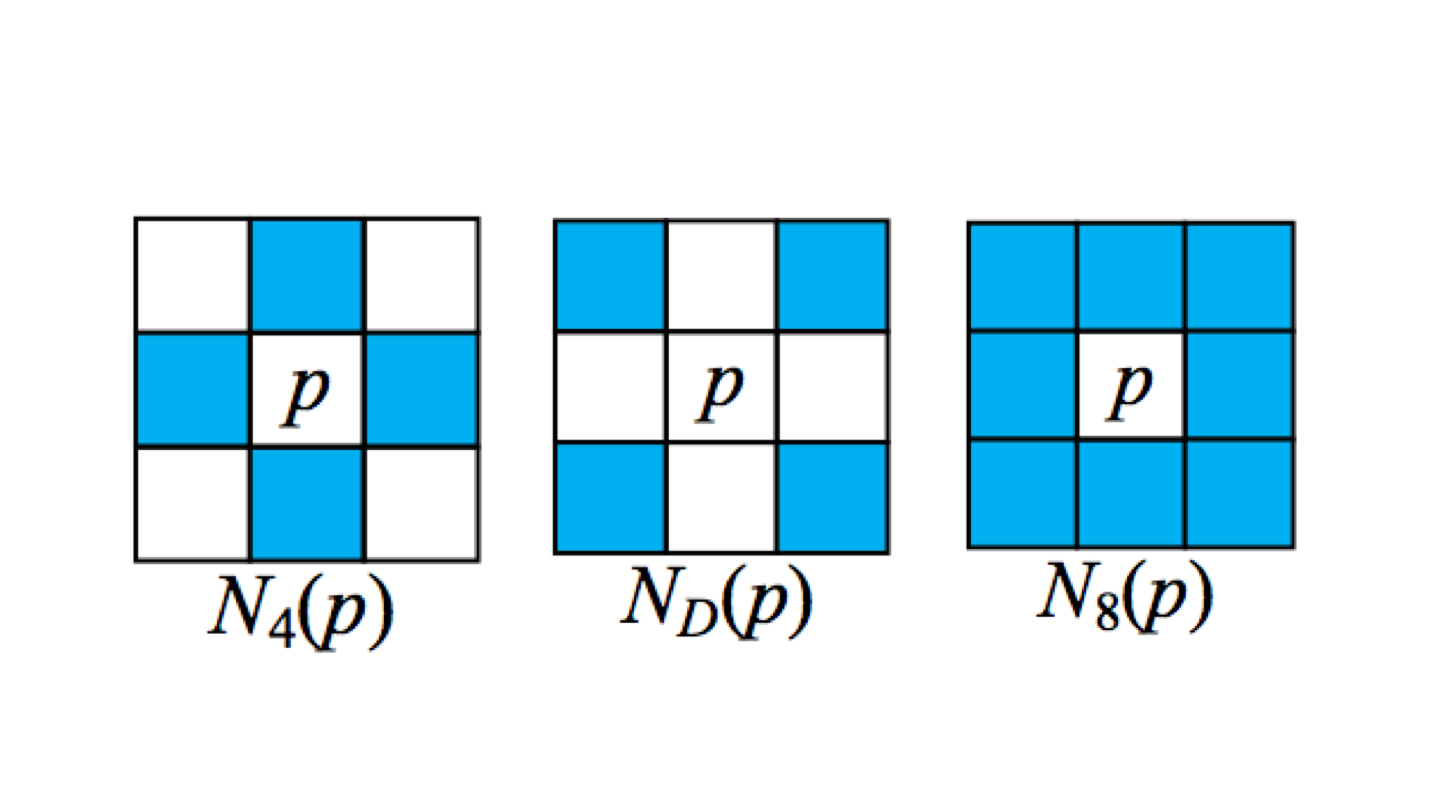
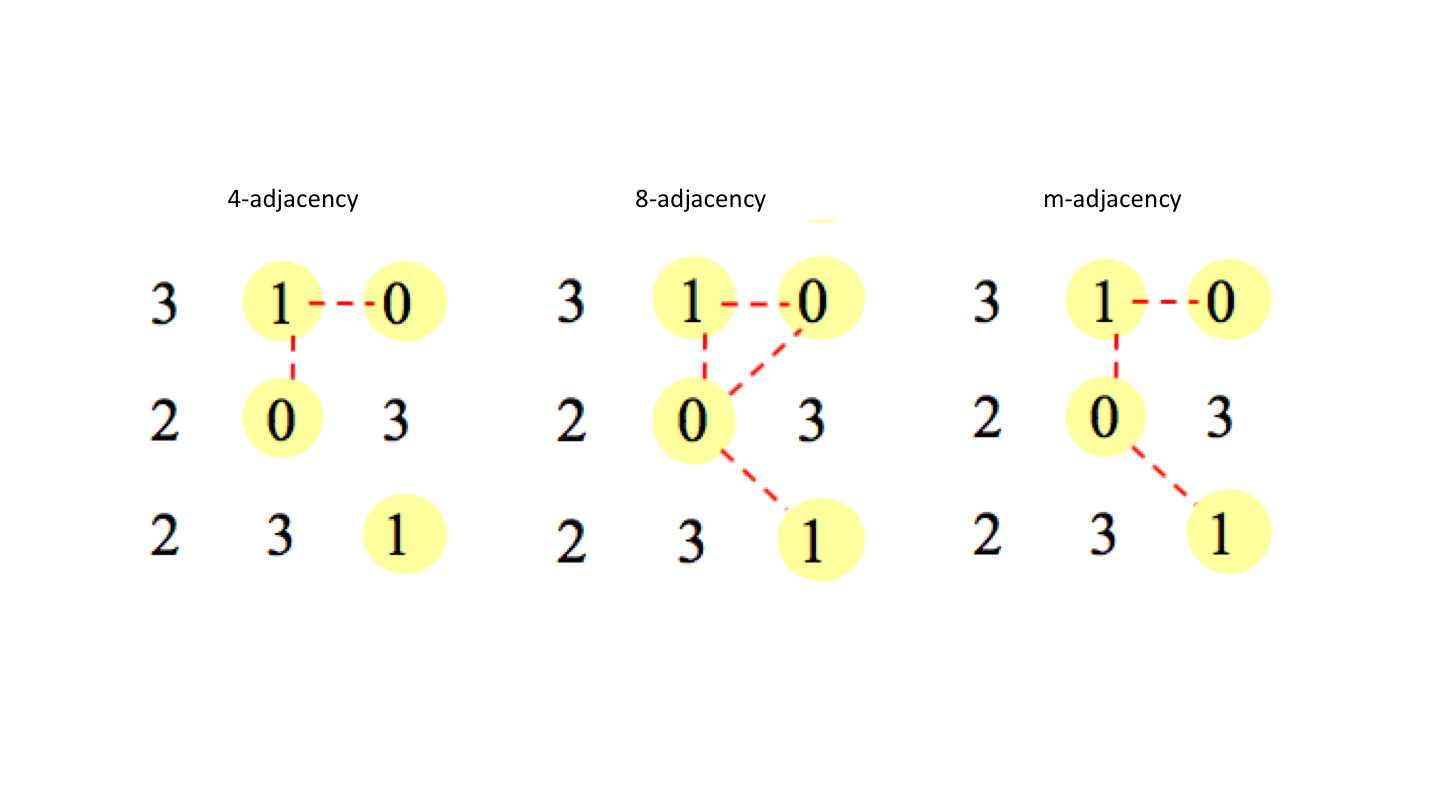
Adjacency
Set of gray-level values V for defining adjacency.
- 4-adjacent
qin set $$N_4(p)$$
- 8-adjacent
qin set $$N_8(p)$$
- m-adjacent
qin set $$N_4(p)$$qin set $$N_D(p)$$ and set $$N_4(p) \cap N_4(q)$$ has no pixels with values fromV
 Set Adjacency
Set Adjacency
2 image subsets $$S_1$$ and $$S_2$$ are adjacent if some pixel in $$S_1$$ is adjacent to some pixel in $$S_2$$.
- 4-adjacent
- Implies 8-adjacent & m-adjacent
- 8-adjacent
- Doesn't imply m-adjacent
- m-adjacent
Path
A sequence of pixels where $$(xi, y_i)$$ and $$(x{i-1}, y_{i-1})$$ are adjacent.
- Length
nforn+1pixels - Closed if $$(x_0, y_0) = (x_n, y_n)$$
Connectivity
A set of pixels S.
- Connected
- There exists a path between
pandqconsisting entirely of pixels inS
- There exists a path between
- Connected component
- The set of pixels mutually adjacent in
S- 4-adjacent
- 8-adjacent
- Implies m-adjacent
- m-adjacent
- The set of pixels mutually adjacent in
- Connected set
- If
Shas only 1 connected component
- If
Distance
- Distance function
D- For pixels
p,q,zat the corners of a triangle:- $$D(p, q) \ge 0$$
- $$D(p, q) = 0$$ iff $$p = q$$
- $$D(p, q) = D(q, p)$$
- $$D(p, z) \le D(p, q) + D(q, z)$$
- For pixels
- Measures
- Euclidean distance
- $$D_e(p, q) = \sqrt{(x - s)^2 + (y - t ^2)}$$
- $$D_4$$ distance (city-block distance)
- $$D_4(p, q) = |x - s| + |y - t|$$
- $$D_8$$ distance (chessboard distance)
- $$D_8(p, q) = max(|x - s|, |y - t|)$$
- $$D_m$$ distance
- Length of shortest m-path
- Euclidean distance
 Logic Operations
Logic Operations
- Negative transformation
- NOT
- Masking / region of interest (ROI) processing: selecting sub-images in an image
- AND
- OR

 Arithmetic Operations
Arithmetic Operations
- Image averaging
- Addition & division
- Usage
- Noise reduction
- Remove zero-mean uncorrelated noise
- $$\begin{aligned}\bar{g}(x, y) &= \frac{1}{K} \sum^{K-1}{i=0} g_i(x, y) \ &= \frac{1}{K} \sum^{K-1}{i=0} [f(x, y) + ni(x, y)] \ &= \frac{1}{K} \sum^{K-1}{i=0} f(x, y) + \frac{1}{K} \sum^{K-1}_{i=0} n_i(x, y) \ &\approx f(x, y) \ \end{aligned}$$
- Background modeling
- $$B{t+1}(x, y) = \frac{\sum^{K-1}{i=0} wi I{t-i}(x, y)}{\sum^{K-1}_{i=0} w_i}$$
- $$B_{t+1}(x, y) = (1 - \alpha) B_t(x, y) + \alpha I_t(x, y)$$
- Noise reduction
- Image subtraction
- Enhance difference
- Usage
- Change detection
- Rescaling: ensure pixel values within $$[0, L-1]$$
- $$g'(x, y) = (g(x, y) - min(g(x, y))) * \frac{L-1}{max(g(x, y)) - min(g(x, y))}$$
- Usage
- Multiplication
- Usage
- Increase/decrease average gray level
- Gray-level masks
- Usage
Convolution
Convolution is symmetric & associative.
$$ f(x) * g(x) = \int^{\infty}_{-\infty} f(u) g(x-u) du
$$

2D Convolution
$$ f(x, y) * g(x, y) = \int^{\infty}{-\infty}\int^{\infty}{-\infty} f(u, v) g(x-u, y-v) dudv
$$
Discrete
$$ f(x) * g(x) = \frac{1}{M} \sum^{M-1}_{u=0} f(u) g(x-u)
$$
$$ f(x, y) * g(x, y) = \frac{1}{MN} \sum^{M-1}{u=0}\sum^{N-1}{v=0} f(u, v) g(x-u, y-v)
$$
Linear Spatial Filtering
Move a mask/filter/kernel over the pixels and retrieve the sum of products.
$$ I2(x, y) = \sum^a{u=-a} \sum^b_{v=-b} w(y, v) I_1(x-u, y-v)
$$
- Dealing with Borders
- Limiting the excursions of center of mask
- Smaller filtered image
- Paddings (replicating rows & columns)
- Need a lot of replication if mask is big
- Partial filter mask: cut the mask if overflowing
- Limiting the excursions of center of mask
Smoothing Filters
Coefficients sum to 1 (no brightness change after applying).
- Usage
- Blurring
- Noise reduction
 Sharpening Filters
Sharpening Filters
Accomplished by spatial differentiation. Coefficients sum to 0 (output 0 if no difference).
Usage
- Highlight fine details
- Enhance details being blurred
Derivatives of a digital function can be obtained by finite differences.
$$\frac{\partial I}{\partial x}$$
$$I(x+1, y) - I(x, y)$$
$$I(x, y) - I(x-1, y)$$
$$\frac{\partial^2 I}{\partial x^2}$$
- $$I(x+1, y) + I(x-1, y) - 2I(x, y)$$

Laplacian Filter
$$\nabla^2 I = \frac{\partial^2 I}{\partial x^2} + \frac{\partial^2 I}{\partial y^2} = [I(x+1, y) + I(x-1, y) + I(x, y+1) + I(x, y-1)] - 4 I(x, y)$$
Composite Laplacian Mask
To preserve background features. Coefficients sum to 1 (copy original information if no difference).
$$g(x, y)=\left{
\begin{array}{c l}
I(x, y) - \nabla^2 I(x, y) & \text{if center coefficient of mask negative}\
I(x, y) + \nabla^2 I(x, y) & \text{if center coefficient of mask positive}
\end{array}\right .$$

Nonlinear Spatial Filters
Smoothing Filter
Median Filter
Replace pixel value with median of those in the neighborhood. Effective in removing impulse noise / salt-and-pepper noise. Less blurring than linear smoothing filters.

Order-Statistics Filter
Max Filter
Finding the brightest points. Reducing pepper noise.
Min Filter
Finding the darkest points. Reducing salt noise.
Midpoint filter
Mean of max & min. Reducing randomly distributed noise e.g. Gaussian noise or uniform noise.
Color Models
- Primary colors
- Red
- Green
- Blue
- Secondary colors
- Cyan
- Megenta
- Yello
- Color models
- RGB
- Light-emitting device e.g. color monitors
- CMY
- Reflective surface e.g. printers
- YIQ
- e.g. color TV broadcast
- HSI, HSV, etc.
- RGB
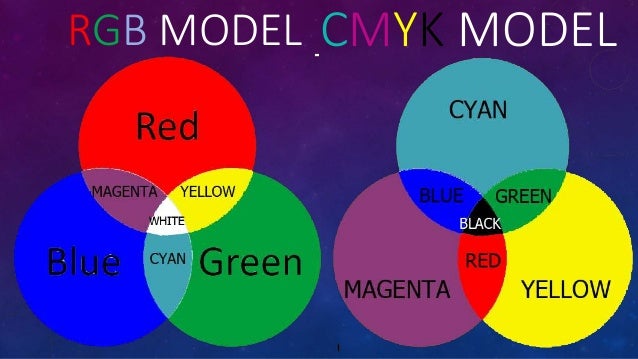
RGB Model
- Each component represented by 8 bits
- Pixel depth 24 bits
- Full-color image
- Gray scale
- Equal portions of R, G, B
YIQ Model
$$ \begin{bmatrix} Y \ I \ Q \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix}
0.299 & 0.587 & 0.114 \ 0.596 & -0.275 & -0.321 \ 0.212 & -0.523 & 0.311 \
\end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} R \ G \ B \end{bmatrix}
$$
- Y
- Luminance
- G larger, similar to human's sense to green light
- All information required by a monochrome TV set
- Sum to 1 (no brightness change after applying)
- Luminance
- I
- Color information
- Sum to 0 (no color information if RGB the same)
- Q
- Color information
- Sum to 0 (no color information if RGB the same)